Uridine Monophosphate is one compound that’s starting to become really popular amongst nootropic lovers. In this article, I’ll share the findings of my research on Uridine Monophosphate – how it works and how it can potentially benefit you. Also, find out how our nootropic stack (Seneca Nootropic Complex) can help maximize Uridine’s nootropic powers!
Table of Contents
What is Uridine Monophosphate and what does it do in the brain?
Uridine is a building block of RNA, which allows the body to make proteins. But Uridine is so much more than just RNA. Once absorbed into the body, Uridine Monophosphate can cross the blood-brain barrier (1, 2).
Once in the brain, Uridine can convert into Uridine Tri Phosphate (UTP). Then it further converts into Cytidine Tri Phosphate (CTP) and CDP Choline. When combined with Diacylglycerol, it turns into Phosphatidylcholine, in a pathway known as the Kennedy Pathway. The pathway is pictured below with the enzymes that catalyze the conversions on the arrows (3).
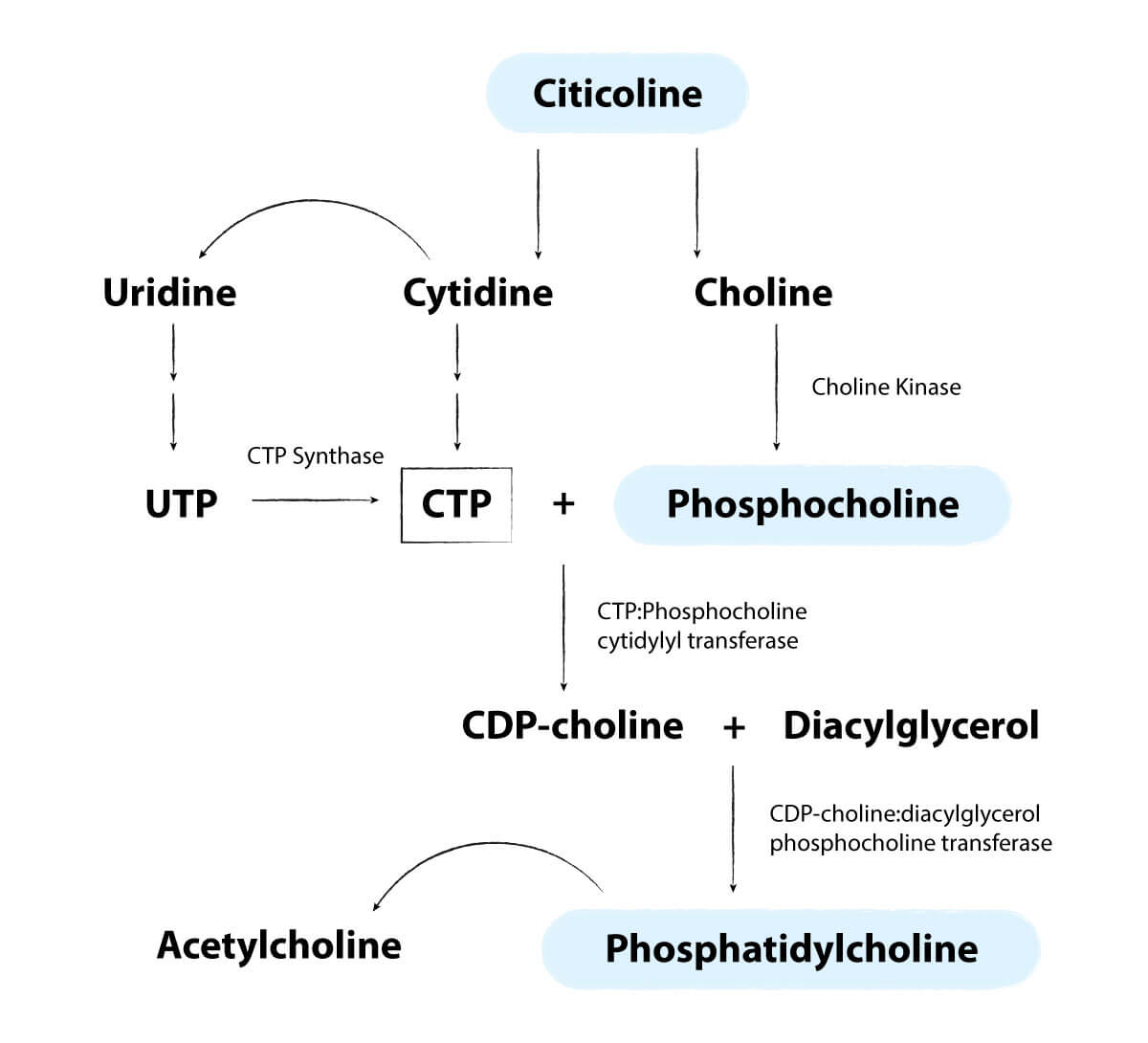
Once we have Phosphatidylcholine, we can produce any of the other 3 main phospholipids. These are Sphingomyelin, Phosphatidylserine, and Phosphatidylethanolamine.
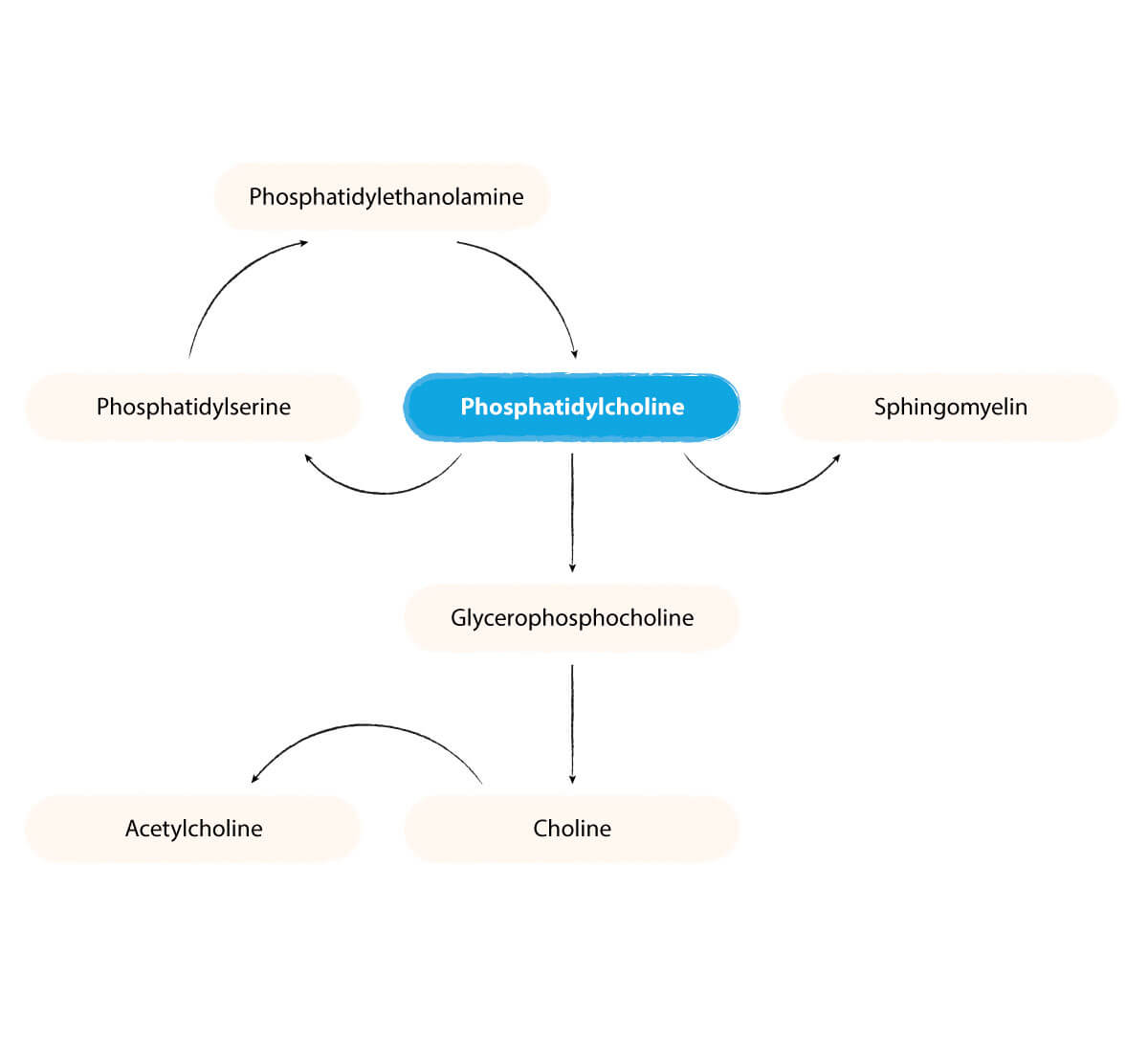
These molecules are critical for health. Phospholipids form the basis of our cell membranes. They are vital for each of our 20 trillion cells and the vast network of communication that takes place between them throughout our body.
Without phospholipids, nothing can get in or out of cells. Phospholipids are also vital for our neurons to grow, repair, and form new connections or synapses with other neurons.
Acetylcholine, aka the “smart” neurotransmitter, helps with focus, attention, memory, and motivation. Its release from neuromuscular junctions allows our brain to contract our muscles.
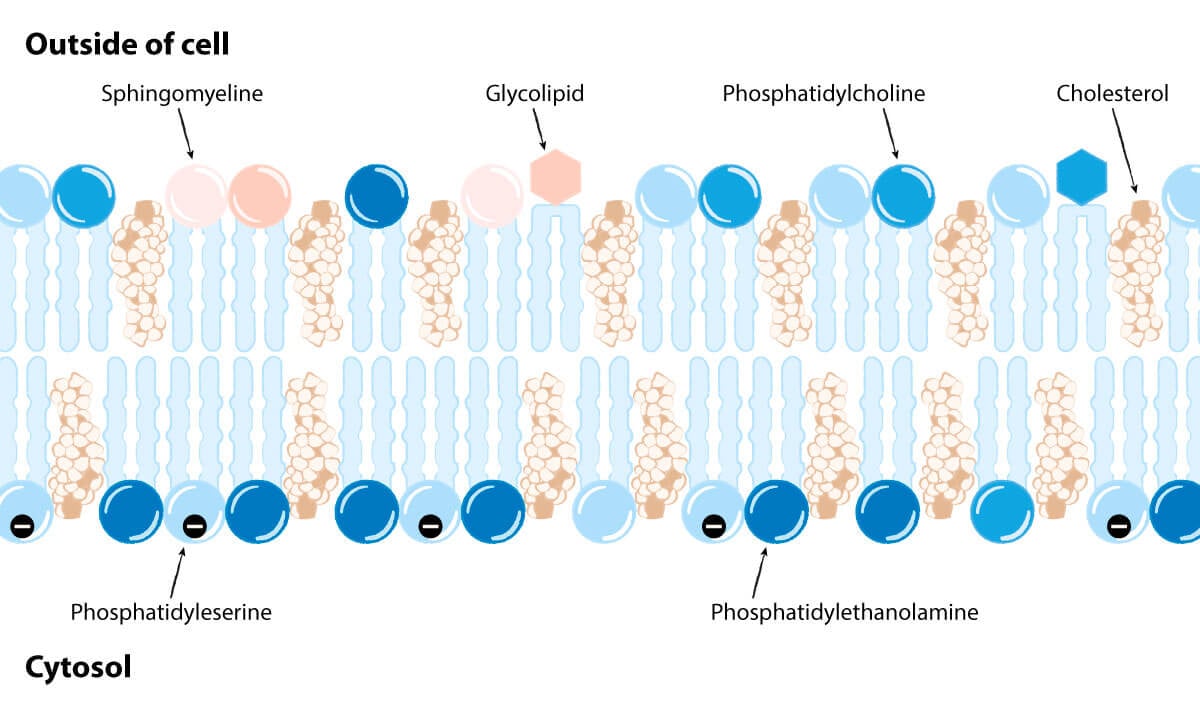
Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin form the outside layer of our cell membranes. Whereas Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine form the inside layer. Here’s what it looks like:
Which is more absorbable? Uridine vs Uridine Monophosphate
Uridine Monophosphate is an important molecule for brain development. It’s found in significant amounts in breast milk and infant formulas (4).
On the other hand, examples of Uridine-rich foods include beer, fish, and broccoli. However, they’re mostly made up of the RNA form, which is not well absorbed in the gut.
Animal studies done by Cansev and Wurtman support Uridine Monophosphate’s superior absorbability (2, 5). Thus, supplementing with Uridine Monophosphate is a good option for those wanting to increase their Uridine levels.
Why take Uridine Monophosphate? Here are 5 benefits
#1 – Uridine can stimulate GABA and Dopamine production
In addition to Uridine’s ability to stimulate synapse, phospholipid production, neuron growth, and acetylcholine production, it can also stimulate Dopamine and GABA production. It also promotes receptor sensitivity to both Dopamine and GABA (6, 7, 8).
Increasing receptor sensitivity means that Dopamine and GABA neurotransmitters can have a greater effect. This means greater focus and motivation because of Dopamine, and more relaxation and peace due to GABA.
#2 – Uridine can help with cognitive development
An animal study selected young rats that were ready to move on from the care of their mothers’. They were kept in either impoverished conditions or enriched conditions for 3 months. Impoverished conditions meant a bare cage, no toys such as ladders, tunnels, swings, and mazes. Meanwhile, enriched conditions meant toys and and other rats to socialize with.
Rats are social animals and thrive when they are able to interact with their environment and learn. So putting them in ‘impoverished’ conditions affects their cognitive development.
That said, all of the rats were fed a full diet. Some were also fed Uridine Monophosphate. The researchers found that the ‘impoverished’ rats not given Uridine had reduced learning and memory. On the other hand, the ‘impoverished’ rats fed with Uridine actually had memory and learning on par with the ‘enriched’ rats (9).
#3 – It can help improve sleep quality
Studies in rats have also found that Uridine benefits include helping with sleep, especially slow-wave or deep sleep (10, 11, 12).
Slow-wave sleep makes up stage 3 of sleep. This stage is necessary for memory consolidation, when short-term memories turn into long-term memories. People with reduced levels of deep sleep tend to struggle more with memory problems.
#4 – It can help with glycogen or energy production
Perhaps one of the least understood benefits of Uridine is its role in the production of glycogen. Glycogen is stored glucose. It gives us an immediate store of energy that can be used whenever it’s needed.
Uridine as Uridine Diphosphate Glucose is a direct precursor to glycogen. It can directly activate glycogen synthesis (13).
Not having enough glycogen can be a problem and can lead to us running out of fuel or ‘hitting the wall’ if we’re exercising. We may also generally feel weak and lose focus at any time during the day.
If it happens overnight, it can lead to us waking up and struggling to go back to sleep. Even for people on fully ketogenic diets, the brain still needs to get around 40% of its energy from glucose / glycogen. So, not being able to make enough glycogen can easily cause cognitive problems.
#5 – Uridine can improve your mood with its antidepressant effect
Carlezon and colleagues did an animal study where they gave either Uridine or Omega-3 fatty acid (specifically DHA) or both to rats. Then they compared them to control rats on a forced swim test. This test helps researchers understand the rats’ emotional states, i.e. if they’re feeling good or not.
The rats are placed in a water-filled plastic cylinder. The longer the animals swim, the better they may be feeling. The test lasts for 15 minutes max or when the animal gives up.
The outcome? Both DHA and Uridine helped increase the rats’ swim time. Both DHA times and Uridine times were similar. Moreover, if both DHA and Uridine were combined, the rats needed less of each to reach the maximum swim time (14)!
That said, synthetic antidepressants can also increase the amount of time the animals swim for. This study confirms that Uridine (and DHA) can indeed help improve mood, working similarly to antidepressants.
What’s the right dosage for taking Uridine?
There is currently no official Uridine monophosphate dosage. As demonstrated by clinical studies, Uridine dosage varies.
For example:
Depressed teenagers with bipolar disorder took 500g of Uridine twice a day. 6 weeks later, the subjects showed an improvement in their symptoms (15).
Meanwhile, another study gave 1g of Uridine twice a day for 1 week to healthy adults. This dosage was enough for the subjects’ to significantly increase their membrane phospholipids. This is important because cognitively impaired individuals often have altered brain phospholipid levels (16).
Stacking Uridine, Choline, and DHA together
Several studies have looked at Uridine, DHA, and Choline-rich diets. If you take these 3 molecules, you theoretically have everything you need to produce new synapses and neuronal growth!
In fact, Alzheimer’s and other cognitive decline patients exhibit a number of different traits. This includes a reduced number of brain synapses, dendritic spines, and membrane-rich structures. But the combination of Uridine, Choline, and DHA may help significantly increase all of these (17, 18, 19). So, the possibility remains that supplementing with these 3 compounds may help prevent dementia.
However, so far the clinical trials in humans have produced somewhat mixed results. They didn’t provide a significant difference in preventing subjects who had mild cognitive impairment (first stage of dementia) from going on to develop dementia or Alzheimers. Nevertheless, the subjects made improvements in cognitive tests on attention, memory, and executive function (20, 21).
It may be a case that by the time symptoms of dementia are actually showing, there is already too much neuronal damage to be able to reverse it. So the benefit of this nutritional therapy could be in prevention.

Want to try this Uridine, Choline, and DHA stack?
If you would like to try this stack, we recommend the following products:
1) Seneca Nootropic, which contains 150mg Uridine Monophosphate, 250mg Citicoline, and 16 other proven nootropics.
2) Ultra Pure Omega 3, which contains 816mg of DHA per 3-capsule serving (along with 1224mg of EPA).
Check out this article on “What Are Nootropics?” to learn more about how nootropics can help you!




